Green Page
Residual gas disposal – playing an active role in environmental protection
gas aktuell No. 35, 1988
Photo: Undiscovered “abandoned toxic waste” still lies dormant on the grounds of some companies.

Green Page
Residual gas disposal – playing an active role in environmental protection
gas aktuell No. 35, 1988
Photo: Undiscovered “abandoned toxic waste” still lies dormant on the grounds of some companies.
Until recently, toxic, corrosive or flammable gases left over in cylinders with an expired inspection tag posed an insurmountable problem for the user. Messer Griesheim has been working hard on a comprehensive disposal concept for such “abandoned toxic waste” since the 1970s. This concept includes selecting suitable disposal processes, establishing a disposal facility, and providing safe transport modalities. The final missing piece of the system was put in place with a nationwide transport authorization pursuant to German regulations governing hazardous goods and waste management. Since February 1987, Messer Griesheim is the only gas supplier that can perform the legally compliant disposal of residual gas within the Federal Republic of Germany – from the evaluation and transport to the actual disposal of the compressed gas tanks.
When leftovers become a problem
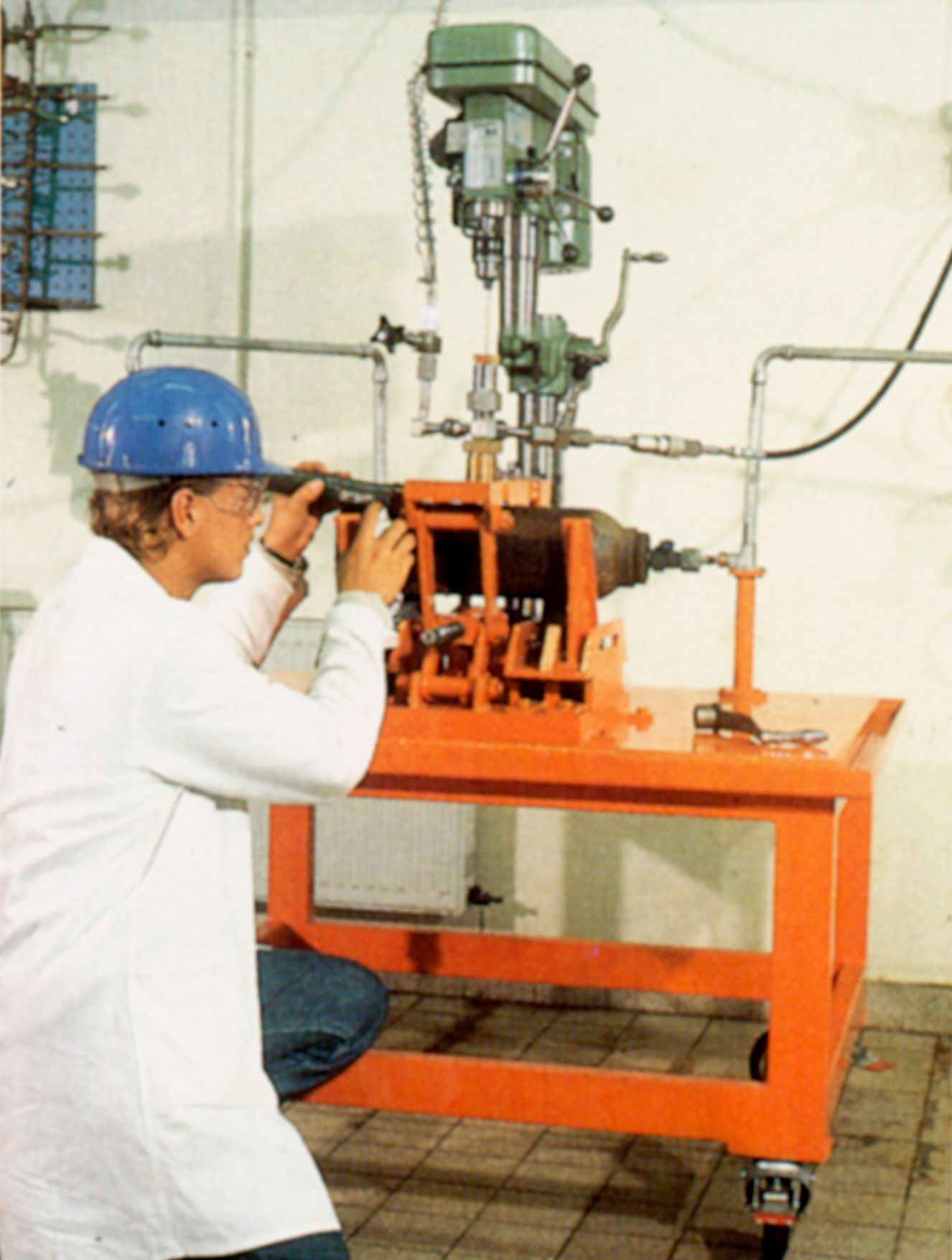
Corrosive and toxic gases are indispensable prerequisites for many production processes. As the residual contents of compressed gas tanks gathering dust in some forgotten corner, they represent no small hazard potential. Tanks are often heavily corroded, the valve is no longer functional, and, only in rarest of cases can the user properly dispose of the residual contents on site.
Authorizations and legal bases
The disposal facility must comply with § 7 Para. 2 of the German Waste Disposal Act and ensure that selected materials can be safely disposed of using verified processes and in compliance with applicable safety regulations. For that reason, the authorization procedure for such a facility is complex and subject to compliance with many ancillary provisions. At Messer Griesheim, an authorized facility has existed (Disposer No. E 1121502) for 36 substances since 1984.
Hazardous goods legislation
According to § 5 German Regulation on Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (GGVS), compressed gas cylinders subject to mandatory inspection may remain in service for an unlimited period of time but can no longer be transported. Derogations for individual transports are possible upon presentation of an expert assessment from TÜV (Technical Inspection Association). In February 1987, Messer Griesheim obtained a general derogation that is valid throughout Germany pursuant to § 5 GGVS. The suitability of cylinders for transport is assessed by MGI specialists without the need to involve a TÜV expert.
Waste legislation
When the proprietor of a compressed gas tank containing residual gas no longer wants to retain possession of it, the tank must be treated as waste pursuant to the German Waste Act (AbfG). For each transport, an authorization pursuant to § 12 AbfG must be granted by the authorities of the German federal state in whose jurisdiction the carriage starts.
The only exception to this mandatory individual authorization is for cylinders whose contents can be disposed of in a facility approved pursuant to § 7 Para. 2 AbfG. The waste generators, the transporter and the waste disposer must – pursuant to the German Waste Documentation Ordinance (Abf Nachw. V) – continuously document the whereabouts of the waste (waste consignment note). In February 1987, Messer Griesheim obtained a waste transport authorization that is valid throughout Germany (Authorization E 18703230 and Waste Transporter No. E 1118119).
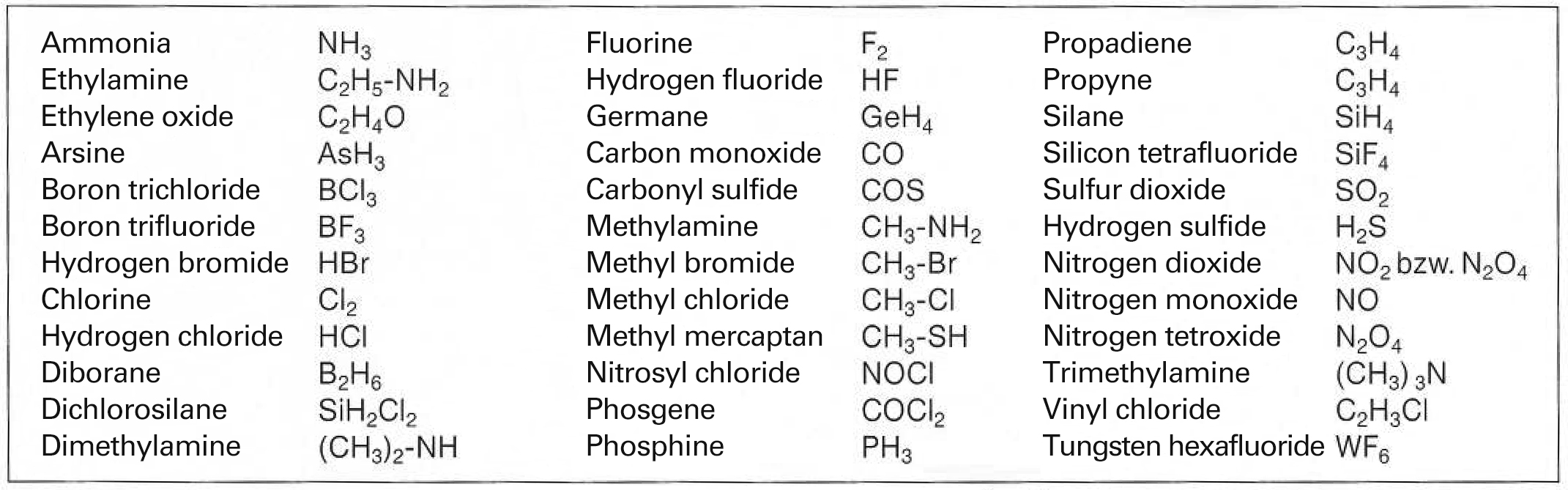
Gases that can be disposed of in the plant operated by Messer Griesheim
Disposal processes
The residual gas disposal facility developed by Messer Griesheim comprises several standalone units that work according to different processes. That differentiation is necessitated by the wide range of properties of the gases to be disposed of. Basically, the following processes were selected:
- Absorption with absorption solutions in scrubbers
- Thermal decomposition
- Thermal decomposition with dust collection
- Adsorption and absorption on solid sorbents
- Oxidation from NO to NO₂
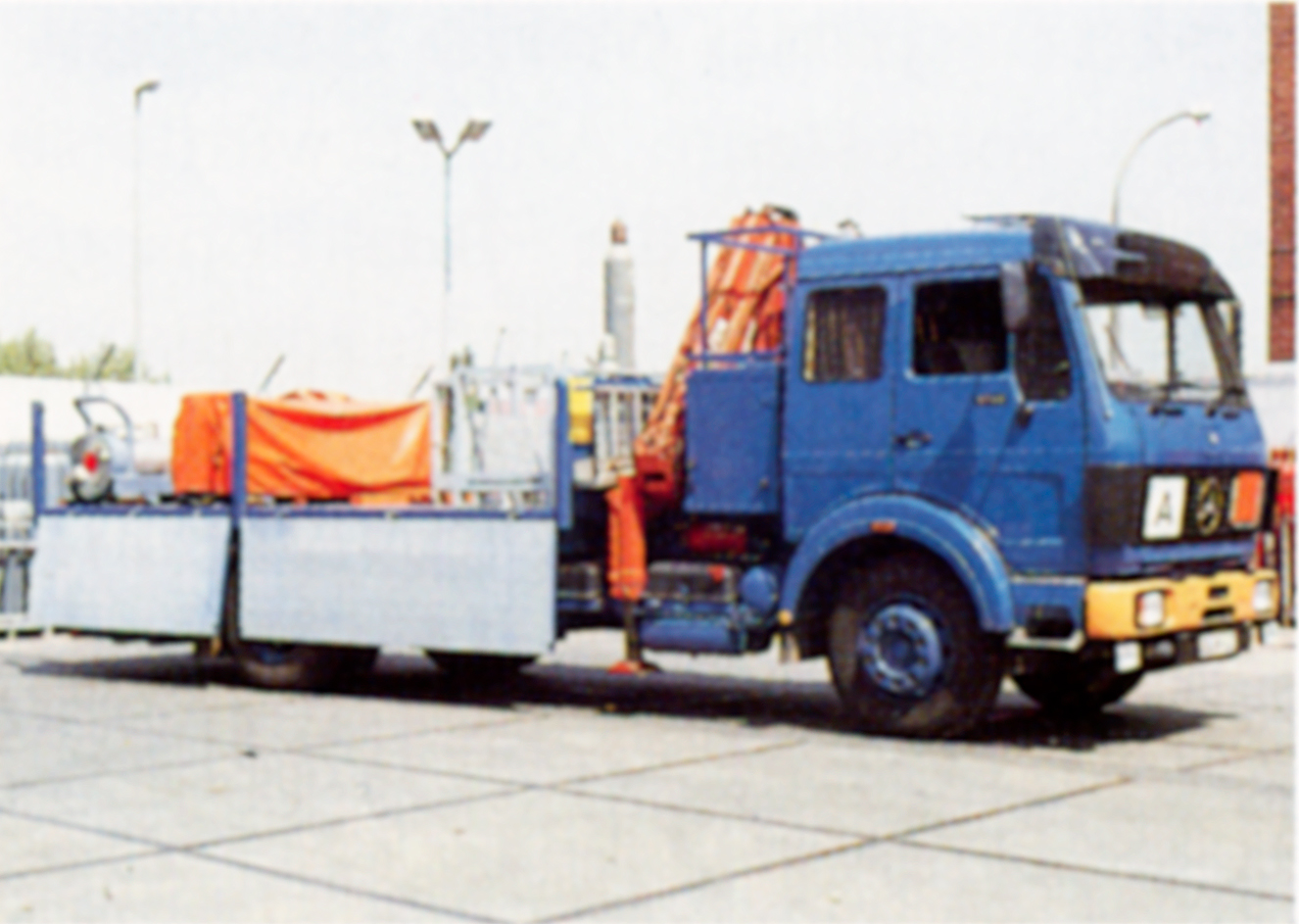

Special vehicle for residual gas disposal
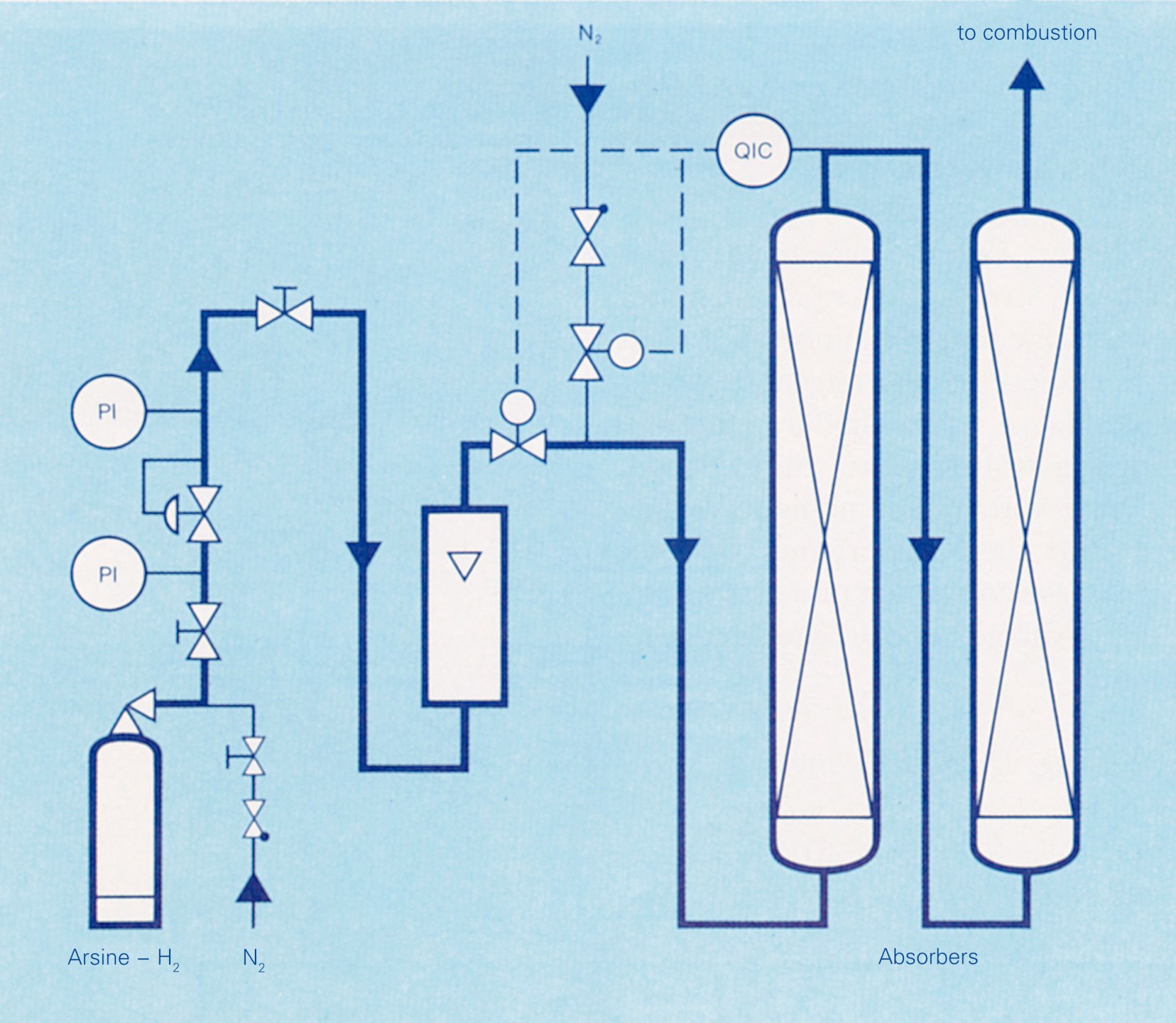
Residual gas disposal by means of alkali scrubbing
Worry-free disposal
The plant was designed to ensure that its reaction products will have a negligible adverse effect on the environment. A careful analysis studied the following possible effects:
- Emission of pollutants
- Odors
- Wastewater pollution
- Generation and deposition of toxic solids.
Harmful emissions and odors are prevented by nearly complete chemical transformations, with residual emissions remaining well below the maximum permissible values specified by German Clean Air Regulations (TA Luft). The processes carried out produce used absorption solutions with dissolved reaction products in the form of salts or depleted solid sorbents. Any solutions that form are collected in wastewater tanks, analyzed, tested for pH neutrality and adjusted if necessary. After suitable dilution, the neutralized solutions can be discharged to the public sewer system. The relevant steps are registered and documented. Waste recycling services or downstream industrial branches must be engaged when solid bed reactors are used.
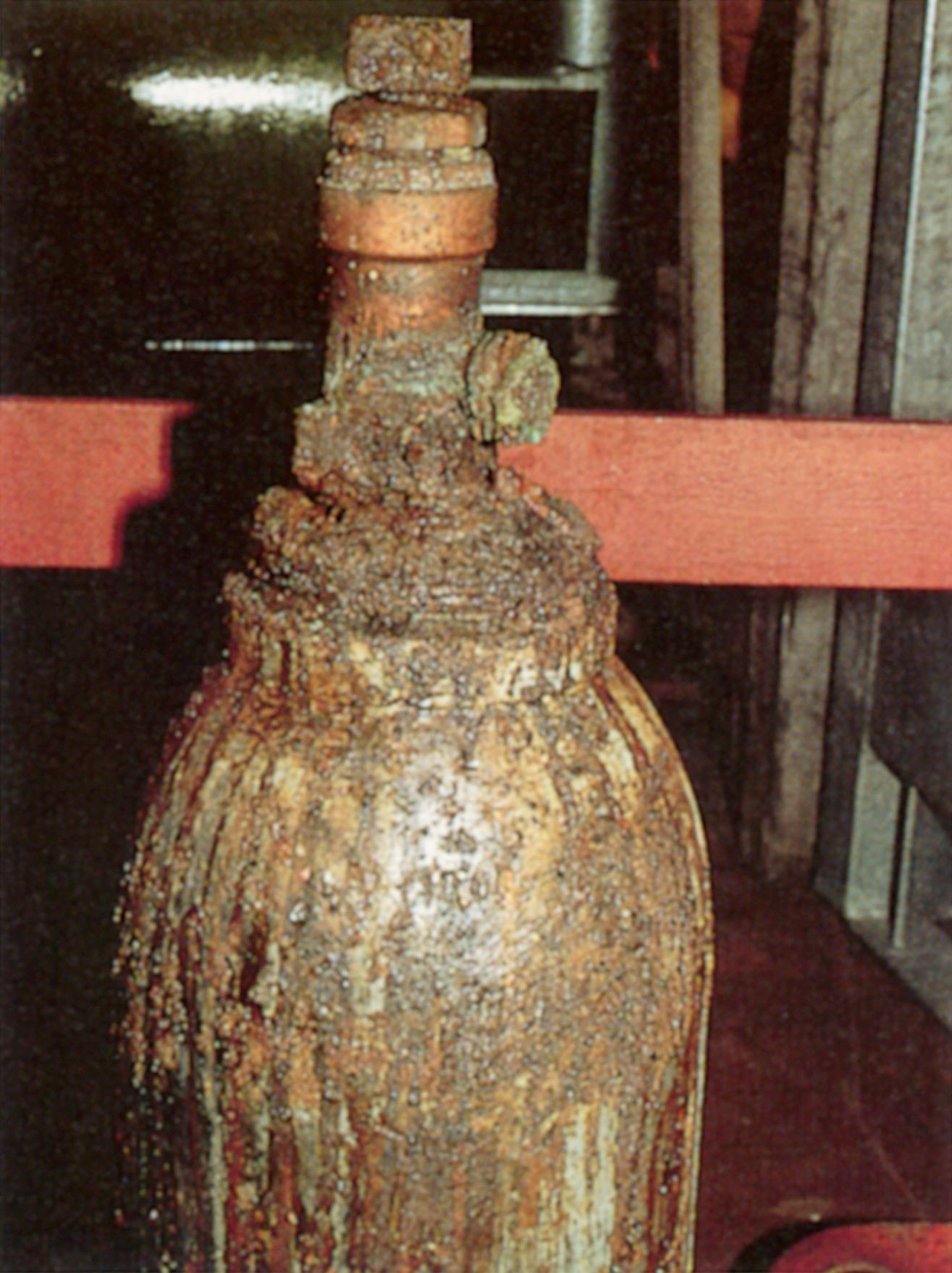

Cylinder with severely damaged valve

